According to the Sliding Filament Model of Muscle Contraction
The mechanism of muscle contraction is explained by sliding filament model. The diagram above shows part a myofibril called a sarcomere.

Sliding Filament Theory Of Muscle Contraction Online Biology Notes Muscle Contraction Biology Notes Muscle
The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement.

. Calcium must be released from the endoplasmic reticulum. C A bands bunch up and shorten as myosin heads attach to. -actin monomers can bind with myosin actin has a myosin-binding site -they are arranged in an orderly repeating fashion.
According to the sliding filament theory how does muscle contraction occur. Simply put the sliding-filament theory happens as follows. B Both thick and thin filaments shorten as the muscle contracts.
Instead they slide by one another causing the sarcomere to shorten while the filaments remain the same length. Move the z-lines apart b. These observations led them to propose the sliding filament theory or the muscle contraction theory.
For a muscle cell to contract the sarcomere must shorten. Actin filaments slide inward on myosin drawing the Z-lines toward the center of the sarcomere and shortening the muscle fiber. Move the z-lines together e.
The sliding filament theory is a suggested mechanism of contraction of striated muscles actin and myosin filaments to be precise which overlap each other resulting in the shortening of the muscle fibre length. The theory states that the sliding of actin past myosin generates muscle tension. The sliding filament model describes the process used by muscles to contract.
According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction 648209666. The sliding filament theory describes the mechanism that allows muscles to contract. When a muscle contracts the distance between the Z discs is reducedThe A band does not shortenit remains the same lengthbut A bands of different sarcomeres move closer together during contraction eventually disappearing.
According to this theory myosin a motor protein binds to actin. This mechanism is explained by the sliding filament theory. The sliding filament theory.
Myosin heads attach and detach from thin filaments causing thin filaments to shorten. However thick and thin filamentsthe components of sarcomeresdo not shorten. A bands bunch up and shorten as myosin heads attach to thin filaments.
For a skeletal muscle to contract its sarcomeres must shorten in length. During muscle contraction a sarcomere. According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction In which category of muscle of muscle contraction the filament that move to shorten a muscle are.
According to the sliding filament model which of these events occur during muscle contraction. Up to 10 cash back According to the sliding filament theory muscle contraction occurs through the relative sliding of two sets of filaments actin and myosin. The Sliding-Filament Theory of Muscular Contraction.
This sliding is produced by cyclic interactions of sidepieces from the myosin filament cross-bridges with specific sites on the actin filament. The thick and thin filaments do not change. This theory was proposed by HE Huxley and J.
A Myosin heads form cross bridges and pull thin filaments causing them to slide. This process is known as the sliding filament theory. Describe the processes of muscle contraction.
As actin is tethered to structures located at the lateral ends of each sarcomere Z discs or Z bands any shortening of this filament length would result in a shortening of the sarcomere which would in. These filaments slide in and out between each other to form a muscle contraction hence called the sliding filament theory. ATP must be broken down for energy.
According to the sliding filament theory how does muscle contraction occur. The myosin then alters its configuration resulting in a stroke that pulls on the actin filament and causes it to slide across the myosin filament. According to the sliding filament model in order for a sarcomere to contract.
What is the sliding filament model for muscle contraction. The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction was developed to fit the. At a very basic level each muscle fibre is made up of smaller fibres called myofibrils.
Both thick and thin filaments shorten as the muscle contracts. Myosin filaments break down ATP myosin filaments form cross bridges that pull on actin actin filaments are pulled toward the center of the sarcomere. The arrangement of actin and myosin myofilament within a sarcomere is crucial in the mechanism of muscle contraction.
Move the z-lines apart d. According to the sliding filament theory when a muscle cell contracts the thin filaments slide past the thick filaments and the sarcomere shortens. A sarcomere is defined as the distance between two consecutive Z discs or Z lines.
Bridges must form between actin and myosin. Shorten the thin filaments. Evidence for the sliding filament theory.
According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction myosin heads pull on _____ filaments and _____. It is a cycle of repetitive events that causes actin and myosin myofilaments to slide over each other contracting the sarcomere and generating tension in the muscle. According to the sliding filament theory the myosin of muscle fibers slide past the actin during muscle contraction while the two groups of filaments remain at relatively constant length.
The theory was independently. Actin thin filaments combined with myosin thick filaments conduct cellular movements. These contain even smaller structures called actin and myosin filaments.
Calcium is thus released throughout the muscle producing a coordinated contraction. All of the above. It is proposed that muscle contracts by the actin and.
Each such interaction is associated with a cross-bridge power stroke. Instead they slide past one another causing the sarcomere to shorten. Move the z-lines together c.

A Level Biology Revision Muscle Contraction Muscular System Biology Revision

Muscle Contraction Modeling Sliding Filament Theory With Paper Cutouts And White High School Science Activities Anatomy And Physiology High School Activities
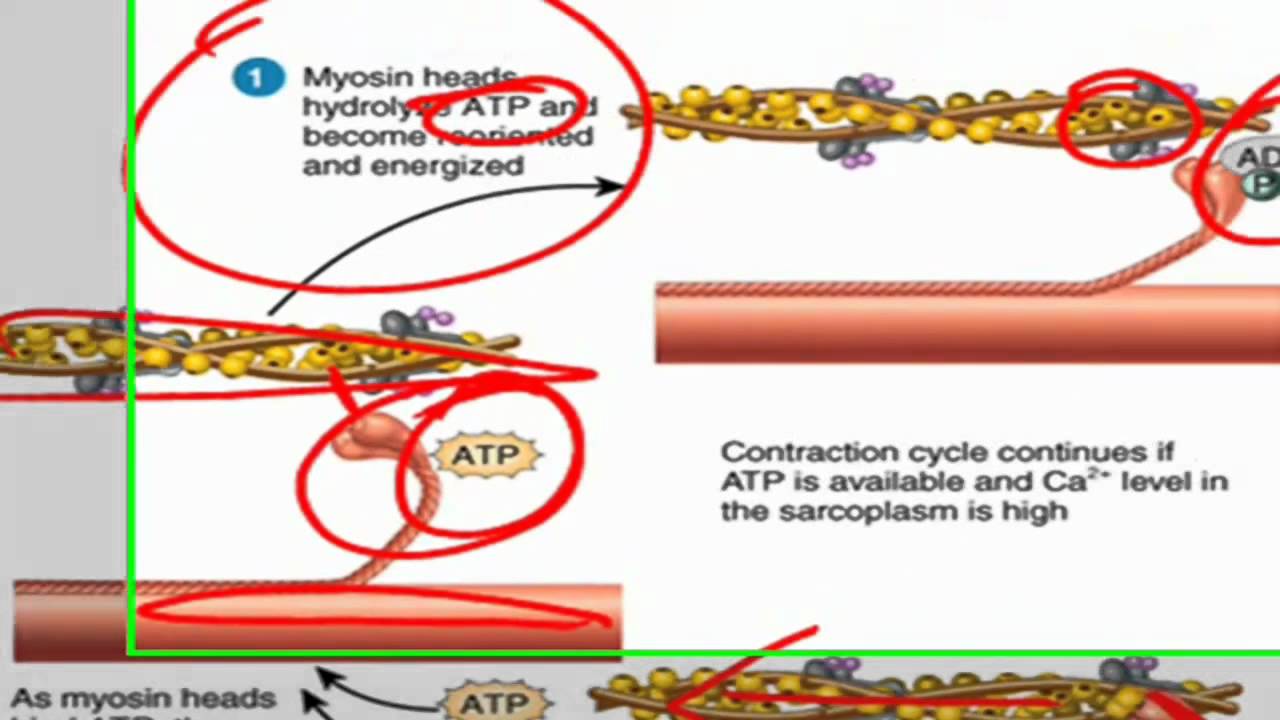
Sliding Filament Theory Of Muscle Contraction Video Human Body Systems Muscular System Body Systems

Myosin Crossbridge Cycle Physiology Anatomy Study A Level Biology

Muscle Contraction And Relaxation Interdigitation Of Thick And Thin Filaments Allows Sarcomere Basic Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Anatomy And Physiology

Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Muscle Contraction Physiology Medical Student Study

47 6 The Release Of Ca2 From The Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Triggers Muscle Contraction When Muscle Contraction Human Muscle Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology

Sarcomere Definition Structure Sliding Filament Theory Basement Membrane Plasma Membrane Nursing Study

Thefatstudent 9 32pm Sliding Filament Theory Of Muscle Contraction Poster To Go On My Revision Biology Revision How To Study Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology

Notes Muscles Medical Anatomy Medical Student Study Study Biology

Biology Sliding Filament Model Lesson Activities Lessons Activities Biology Classroom Biology Lessons

Chapter 12 Basic Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology

Sarcomere Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia Physiology Nursing School Studying Exercise Physiology

Notes Muscles Neuromuscular Junction Human Body Unit Study Medical Student Study

Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Online Biology Notes Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Basic Anatomy And Physiology

Sliding Filament Theory Of Skeletal Muscle Muscle Contraction Filament Skeletal Muscle

Flashcards Table On Structure And Function Of The Muscular Nervous And Skeletal Systems Physiology Muscle Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology

Genius Annotation Of The Sliding Filament Theory Is A Model Of Explaining How Muscle Contraction Act Muscular System Muscle Contraction Musculoskeletal System
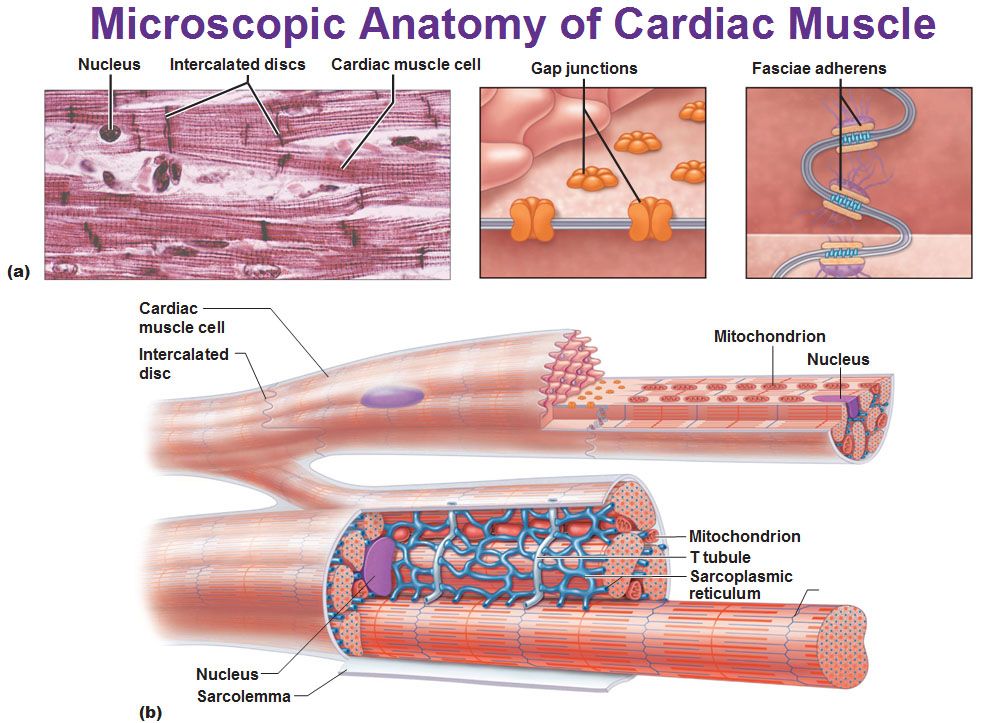
Comments
Post a Comment